Integrating Engineering and the Human Factor (info@uffmm.org)
eJournal uffmm.org ISSN 2567-6458, March 3-4, 2021,
Author: Gerd Doeben-Henisch
Email: gerd@doeben-henisch.de
Last change: March 4, 2021, 07:49h (Minor corrections; relating to the UN SDGs)
HISTORY
As described in the uffmm eJournal the wider context of this software project is an integrated engineering theory called Distributed Actor-Actor Interaction [DAAI] further extended to the Collective Man-Machine Intelligence [CM:MI] paradigm. This document is part of the Case Studies section.
HMI ANALYSIS, Part 4: Tool based Actor Story Development with Testing and Gaming
Context
This text is preceded by the following texts:
- HMI Analysis for the CM:MI paradigm. Part 3. Actor Story and Theories (Feb 3, 2021)
- HMI ANALYSIS, Part 2: Problem & Vision (Feb 27, 2021 at 11:30h)
- HMI Analysis for the CM:MI paradigm. Part 1 (Feb 25, 2021 at 12:08)
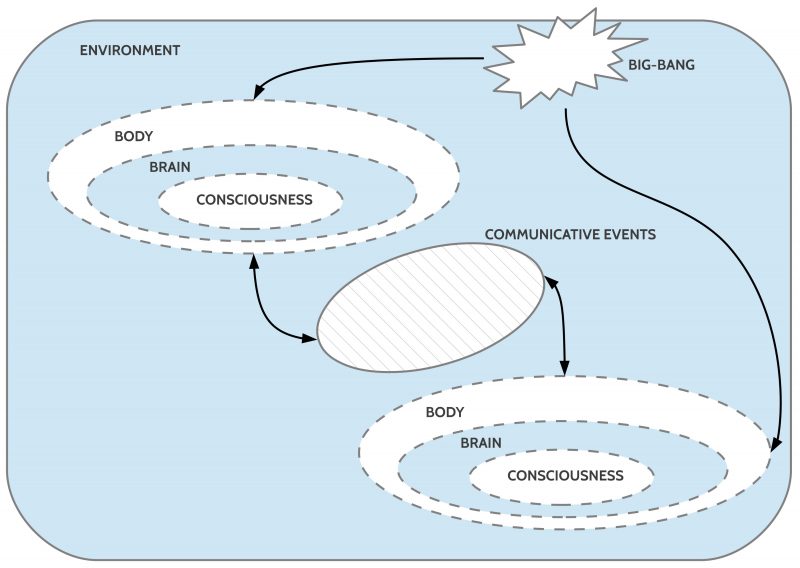
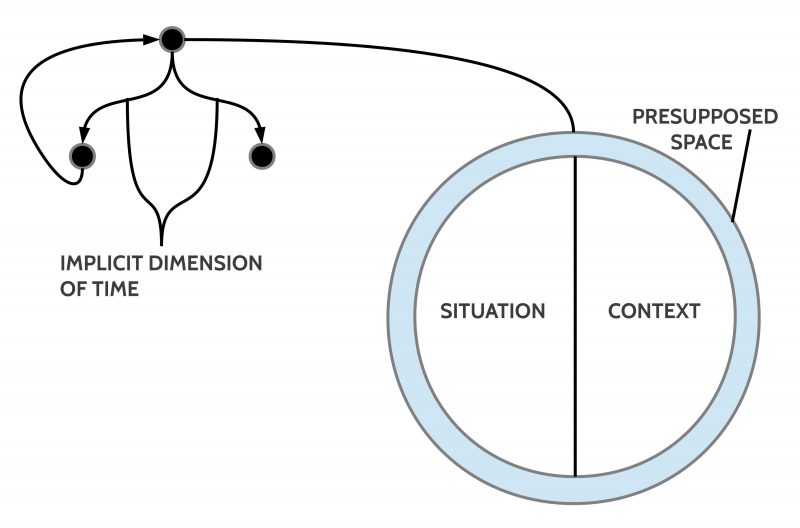
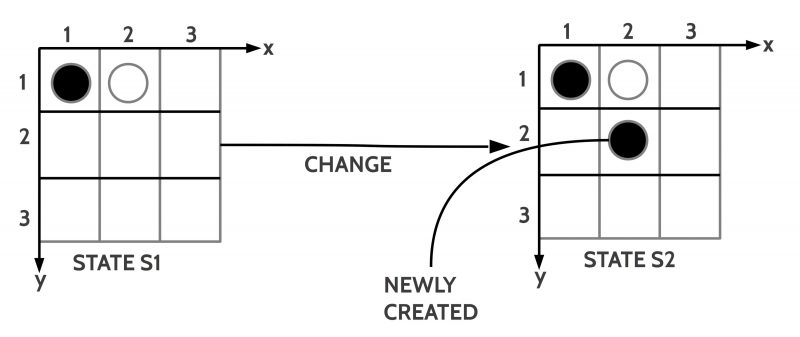
INFO GRAPH
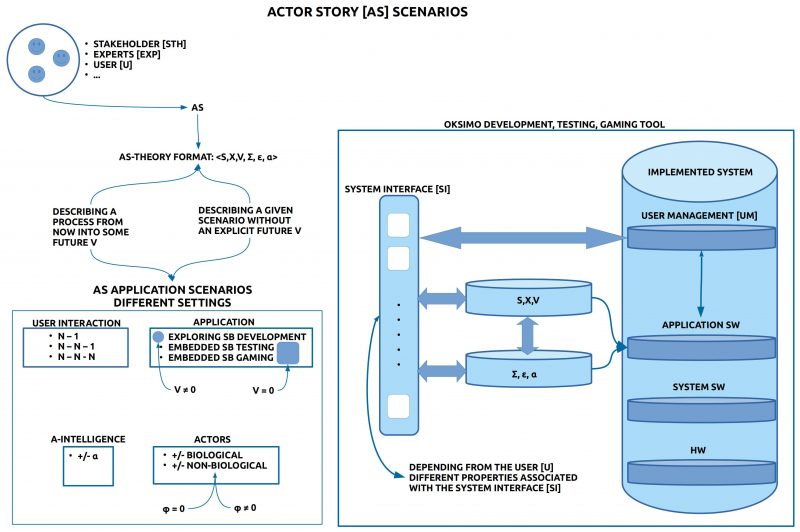
Introduction
In the preceding post it has been explained, how one can format an actor story [AS] as a theory in the format of an Evaluated Theory Tε with Algorithmic Intelligence: Tε,α=<M,∑,ε,α>.
In the following text it will be explained which kinds of different scenarios will be possible to elaborate, to simulate, to test, and to enable gaming with an actor story theory by using the oksimo software tool.
UNIVERSAL TEAM
The classical distinctions between certain types of managers, special experts and the rest of the world is given up here in favor of a stronger generalization: everybody is a potential expert with regard to a future, which nobody knows. This is emphasized by the fact, that everybody can use its usual mother tongue, a normal language, every language. Nothing more is needed.
BASIC MODELS (S, X)
As minimal elements for all possible applications it is assumed here that the experts define at least a given situation (state) [S] and a set of change rules [X].
The given state S is either (i) taken as it is or (ii) as a state which should be improved. In both cases the initial state S is called the start state [S0].
The change rules X describe possible changes which transform a given state S into a changed successor state S’.
A pair of S and X as (S,X) is called a basic model M(S,X). One can define as many models as one wants.
A DIRECTION BY A VISION V
A vision [V] can describe a possible state SV in an assumed future. If such a state SV is given, then this state becomes a goal state SGoal. In this case we assume V ≠ 0. If no explicit goal is given, then we assume V = 0.
DEVELOPMENT BY GOALS
If a vision is given (V ≠ 0), then the vision can be used to induce a direction which can/ shall be approached by creating a set X, which enables the generation of a sequence of states with the start state S0 as first state followed by successor state Si until the goal state SGoal has been reached or at least it holds that the goal state is a subset of the reached state: SGoal ⊆ Sn.
It is possible to use many basic models M(S,X) in parallel and for each model Mi one can define a different goal Vi (the typical situation in a pluralistic society).
Thus there can be many basic theories T(M,V) in parallel.
STEADY STATES (V = 0)
If no explicit visions are defined (V = 0) then every direction of change is allowed. A basic steady state theory T(M,V) with V = 0 can be written as T(M,0). Whether such a case can be of interest is not clear at the moment.
BASIC INTERACTION PATTERNS
The following interaction modes are assumed as typical cases:
- N-1: Within an online session an interactive webpage with the oksimo software is active and the whole group can interact with the oksimo software tool.
- N-N-1: N-many participants can individually login into the interactive oksimo website and being logged in they can collaborate within the oksimo software with one project.
- N-N-N: N-many participants can individually login into the interactive oksimo website and there everybody can run its own process or can collaborate in various ways.
The default case is case (1). The exact dates for the availability of modes (2) – (3) depends from how fast the roadmap can be realized.
BASIC APPLICATIONS
- Exploring Simulation-Based Development [ESBD] (V ≠ 0): If the main goal is to find a path from a given state today S (Now) to an envisioned state V in the future then one has to collect appropriate change rules X to approach the final goal state SGoal better and better. Activating the simulator ∑ during search and construction phase at will can be of great help, especially if the documents (S, X, V) are becoming more and more complex.
- Embedded Simulation-Based Testing [ESBT] (V ≠ 0): If a basic actor story theory T(M,∑) is given with a given goal (V ≠ 0) then it is of great help if the simulation is done in interactive mode where the simulator is not applying the change rules by itself but by asking different logged in users which rule they want to apply and how. These tests show not only which kinds of errors will occur but they can also show during n-many repetitions to which degree an user can learn to behave task-conform. If the tests will not show the expected outcomes then this can point to possible deficiencies of the software as well to specialties of the user.
- Embedded Simulation-Based Gaming [ESBTG] (V ≠ 0): The case of gaming is partially different to the case of testing. Although it is assumed here too that at least one vision (goal) is given, it is additionally assumed that there exists a competition between different players or different teams. Different to testing exists in gaming according to the goal(s) the role of a winner: that player/ team which has reached a defined goal state before the other player/ teams, has won. As a side-effect of gaming one can also evaluate the playing environment and give some feedback to the developers.
ALGORITHMIC INTELLIGENCE
- Case ESBD, T(S,X,V,∑,ε,α): Because a normal simulation with the simulator ∑ always does produce only one path from the start state to the goal state it is desirable to have an algorithm α which would run on demand as many times as wanted and thereby the algorithm α would search for all possible paths and at the same time it would look for those derivations, where the goal state satisfies with ε certain special requirements. Thus the result from the application of α onto a given model M with the vision V would generate the set SV* of all those final states which satisfy the special requirements.
- Case ESBG, T(S,X,V,∑,ε,α): The case of gaming allows at least three kinds of interesting applications for algorithmic intelligence: (i) Introduce non-biological players with learning capabilities which can act simultaneously with the biological players; (ii) Introduce non-biological players with learning capabilities which have to learn how to support, to assist, to train biological player. This second case addresses the challenging task to develop algorithmic tutors for several kinds of learning tasks. (iii) Another variant of case (ii) is to enable the development of a personal algorithmic assistant who works only with one person on a long-term basis.
The kinds of algorithmic Intelligence in (2)(i)-(iii) are different to the mentioned algorithmic intelligence α in (1).
TYPES OF ACTORS
As the default standard case of an actor it is assumed that there are biological actors, usually human persons, which will not be analyzed with their inner structure [IS]. While the behavior of every system — and therefore any biological system too — can be described with a behavior function φ: I x IS —> IS x O (if one has all the necessary knowledge), in the default case of biological systems no behavior function φ is specified, φ = 0. During interactive simulations biological systems act by themselves.
If non-biological actors are used — e.g. automata with a certain machine program (an algorithm) — then one can use these only if one has a fully specified behavior function φ. From this follows that a change rule which is associated with a non-biological actor has in its Eplus and in its Eminus part not a concrete expression but a variable, which will be computed during the simulation by the non-biological actor depending from its input and its behavior function φ: φ(input)IS=(Eplus, Eminus)IS.
FINAL COMMENT
Everybody who has read the parts (1) – (4) has now a general knowledge about the motivation to develop the oksimo software tool to support human kind to have a better communication and thinking of possible futures and a first understanding (hopefully :-)) how this tool can work. Reading the UN sustainable development goals [SDGs] [1] you will learn, that the SDG4 (Ensure inclusive and equitable quality education and promote lifelong learning opportunities for all) is fundamental to all other SDGs. The oksimo software tool is one tool to be of help to reach these goals.
REFERENCES
[1] The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, adopted by all United Nations Member States in 2015, provides a shared blueprint for peace and prosperity for people and the planet, now and into the future. At its heart are the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which are an urgent call for action by all countries – developed and developing – in a global partnership. They recognize that ending poverty and other deprivations must go hand-in-hand with strategies that improve health and education, reduce inequality, and spur economic growth – all while tackling climate change and working to preserve our oceans and forests. See PDF: https://sdgs.un.org/sites/default/files/publication/21252030%20Agenda%20for%20Sustainable%20Development%20web.pdf
[2] UN, SDG4, PDF, Argumentation why the SDG4 ist fundamental for all other SDGs: https://sdgs.un.org/sites/default/files/publications/2275sdbeginswitheducation.pdf