eJournal: uffmm.org,
ISSN 2567-6458, 12.May – 18.Jan 2020
Email: info@uffmm.org
Author: Gerd Doeben-Henisch
Email: gerd@doeben-henisch.de
HISTORY OF THIS PAGE
See end of this page.
CONTEXT
This Theory of Engineering section is part of the uffmm science blog.
HISTORY OF THE (D)AAI-TEXT
See below
ACTUAL VERSION
DISTRIBUTED ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [DAAI]. Version 15.06, From Dec 13, 2019 until Jan 18, 2020
aaicourse-15-06-07(PDF, Chapter 8 new (but not yet completed))
aaicourse-15-06-05(PDF, Chapter 7 new)
aaicourse-15-06-04(PDF, Chapter 6 modified)
aaicourse-15-06-03(PDF, Chapter 5 modified)
aaicourse-15-06-02(PDF, Chapter 4 modified)
aaicourse-15-06-01(PDF, Chapter 1 modified)
aaicourse-15-06 (PDF, chapters 1-6)
aaicourse-15-05-2 (PDF, chapters 1-6; chapter 6 only as a first stub)
DISTRIBUTED ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [DAAI]. Version 15.05.1, Dec 2, 2019:
aaicourse-15-05-1(PDF, chapters 1-5; minor corrections)
aaicourse-15-05 (PDF, chapters 1-5 of the new version 15.05)
Changes: Extension of title, extension of preface!, extension of chapter 4, new: chapter 5 MAS, extension of bibliography and indices.
HISTORY OF UPDATES
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 17, 2019 – V.7: aaicourse-17june2019-incomplete
Change: June 19, 2019 (Update to version 8; chapter 5 has been rewritten completely).
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 19, 2019 – V.8: aaicourse-june 19-2019-v8-incomplete
Change: June 19, 2019 (Update to version 8.1; minor corrections in chapter 5)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 19, 2019 – V.8.1: aaicourse-june19-2019-v8.1-incomplete
Change: June 23, 2019 (Update to version 9; adding chapter 6 (Dynamic AS) and chapter 7 (Example of dynamic AS with two actors)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 23, 2019 – V.9: aaicourse-June-23-2019-V9-incomplete
Change: June 25, 2019 (Update to version 9.1; minor corrections in chapters 1+2)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 25, 2019 – V.9.1: aaicourse-June25-2019-V9-1-incomplete
Change: June 29, 2019 (Update to version 10; )rewriting of chapter 4 Actor Story on account of changes in the chapters 5-7)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 29, 2019 – V.10: aaicourse-June-29-2019-V10-incomplete
Change: June 30, 2019 (Update to version 11; ) completing chapter 3 Problem Definition)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 30, 2019 – V.11: aaicourse-June30-2019-V11-incomplete
Change: June 30, 2019 (Update to version 12; ) new chapter 5 for normative actor stories (NAS) Problem Definition)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 30, 2019 – V.12: aaicourse-June30-2019-V12-incomplete
Change: June 30, 2019 (Update to version 13; ) extending chapter 9 with the section about usability testing)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: June 30, 2019 – V.13: aaicourse-June30-2019-V13-incomplete
Change: July 8, 2019 (Update to version 13.1 ) some more references to chapter 4; formatting the bibliography alphabetically)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: July 8, 2019 – V.13.1: aaicourse-July8-2019-V13.1-incomplete
Change: July 15, 2019 (Update to version 13.3 ) (In chapter 9 Testing an AS extending the description of Usability Testing with more concrete details to the test procedure)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: July 15, 2019 – V.13.3: aaicourse-13-3
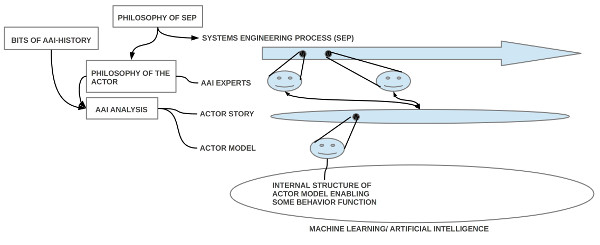
Change: Aug 7, 2019 (Only some minor changes in Chapt. 1 Introduction, pp.15ff, but these changes make clear, that the scope of the AAI analysis can go far beyond the normal analysis. An AAI analysis without explicit actor models (AMs) corresponds to the analysis phase of a systems engineering process (SEP), but an AAI analysis including explicit actor models will cover 50 – 90% of the (logical) design phase too. How much exactly could only be answered if there would exist an elaborated formal SEP theory with quantifications, but there exists no such theory. The quantification here is an estimate.)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version: Aug 7, 2019 – V.14:aaicourse-14
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version 15, Nov 9, 2019:
aaicourse-15(PDF, 1st chapter of the new version 15)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version 15.01, Nov 11, 2019:
aaicourse-15-01 (PDF, 1st chapter of the new version 15.01)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version 15.02, Nov 11, 2019:
aaicourse-15-02 (PDF, 1st chapter of the new version 15.02)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version 15.03, Nov 13, 2019:
aaicourse-15-03 (PDF, 1st chapter of the new version 15.03)
ACTOR ACTOR INTERACTION [AAI]. Version 15.04, Nov 19, 2019:
(update of chapter 3, new created chapter 4)
aaicourse-15-04 (PDF, chapters 1-4 of the new version 15.04)
HISTORY OF CHANGES OF THIS PAGE
Change: May 20, 2019 (Stopping Circulating Acronyms :-))
Change: May 21, 2019 (Adding the Slavery-Empowerment topic)
Change: May 26, 2019 (Improving the general introduction of this first page)
HISTORY OF AAI-TEXT
After a previous post of the new AAI approach I started the first re-formulation of the general framework of the AAI theory, which later has been replaced by a more advanced AAI version V2. But even this version became a change candidate and mutated to the Actor-Cognition Interaction (ACI) paradigm, which still was not the endpoint. Then new arguments grew up to talk rather from the Augmented Collective Intelligence (ACI). Because even this view on the subject can change again I stopped following the different aspects of the general Actor-Actor Interaction paradigm and decided to keep the general AAI paradigm as the main attractor capable of several more specialized readings.